Ovarian Cancer Screening
Ovarian cancer occurs when abnormal cells in your ovaries or fallopian tubes grow and multiply out of control.
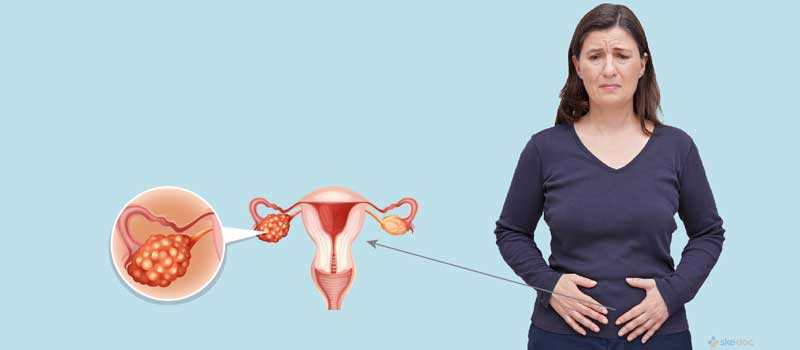
Ovaries are part of the female reproductive system. These two round, walnut-sized organs make eggs during your reproductive years.
Ovarian cancer affects women and people assigned female at birth (AFAB). It’s slightly more common in Native American and white populations than in people who are Black, Hispanic or Asian.
In addition, people of Ashkenazi Jewish descent are much more likely to have a BRCA gene mutation, placing them at a higher risk for breast and ovarian cancer.
Ovarian cancer accounts for 1% of all new cancer cases in the U.S. The lifetime risk of developing ovarian cancer is approximately 1 in 78.
What are the symptoms of ovarian cancer?
Ovarian cancer can develop and spread throughout your abdomen before it causes any symptoms. This can make early detection difficult. Ovarian cancer symptoms may include:
- Pelvic or abdominal pain, discomfort or bloating.
- Changes in your eating habits, getting full early and losing your appetite.
- Vaginal discharge or abnormal bleeding, especially if the bleeding occurs outside of your typical menstrual cycle or after you’ve gone through menopause.
- Bowel changes, such as diarrhea or constipation.
- An increase in the size of your abdomen.
- Peeing more often (frequent urination).